ENTERPRISE SOFTWARE
INTRODUCTION
Computer programs utilized by companies as opposed to private individuals are referred to as enterprise software, or corporate application software. Enterprise resource planning, contact center software, business analytics, enterprise communication, inventory management, marketing tools, and online payments are examples of common enterprise software categories. Enterprise software is used by organizations to create their own custom apps in addition to running, scaling, and optimizing daily operations and processes.
IMPORTANCE OF ENTERPRISE SOFTWARE
In many organizations, enterprise software is essential to both mission-critical and daily business activities. Here are some instances of how businesses make use of enterprise software solutions:
1. Scale resources
Enterprise software helps businesses grow and allocate resources to the right departments. They can adjust their size as needed to reduce expenses, allocate resources sensibly, and adhere to budgetary constraints. For instance, you may integrate scalable communication features like text, voice, and video into your current workplace apps by using the Amazon Chime SDK.
2. Improve organizational efficiency
By automating processes like payroll, marketing, HR, and data entry, enterprise application software frees up staff members to concentrate on work that benefits the company more. It provides a uniform set of workflow solutions and collaborative technologies that lessen departmental silos.
3. Enhance employee productivity
Artificial intelligence (AI), data analytics, machine learning (ML), project management software, process automation, and data analytics are examples of technologies and tools that facilitate team communication and provide useful insights. Teams are able to interact with one another no matter where they are. Employees are able to do daily duties more quickly as a result.
4. Increase customer satisfaction
Organizations can now have a thorough awareness of their customers and their demands thanks to enterprise software solutions like contact center software, marketing automation, and customer relationship management. Businesses can meet customer requests by providing a personalized service experience by centralizing and combining customer data.
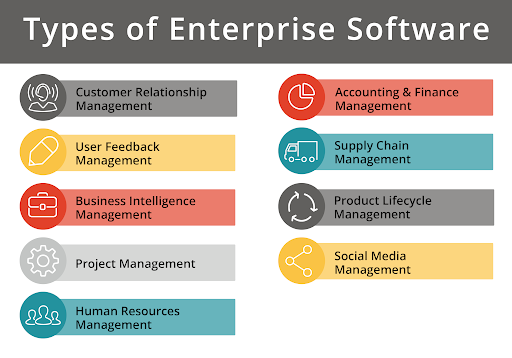
TYPES OF ENTERPRISE SOFTWARE
Enterprise software is offered in a variety of forms and brands. Several major categories can be used to group the software. Below are a few instances.
1. Enterprise resource planning
With the aid of enterprise resource planning (ERP) software, businesses may handle a variety of operations from a single, centralized system, such as payroll, supply chain, HR, and sales. ERP software is used by organizations to:
- Centrally manage organizational data from different sources.
- Automate tasks and simplify business processes.
- Deliver operational efficiency and boost profitability.
2. Customer relationship management
Enterprises use customer relationship management (CRM) and contact center software to:
- Better manage customer relationships.
- Develop insights into customer needs through data.
- Deliver better experiences to existing customers.
- Make informed decisions about new prospects.
3. Business intelligence
Business intelligence refers to enterprise application software that combines data stored in spreadsheets, on-premises data centers, and the cloud for analysis and reporting purposes. Interactive dashboards provide a uniform view of the data for all individuals inside an organization. Additionally, business intelligence software identifies trends and patterns so that groups can:
- Gain valuable insights into business processes.
- Make strategic decisions with confidence.
- Avoid time-consuming manual analysis .
4. Supply chain management
In order to provide goods and services, manufacturers, suppliers, logistics, and retailers collaborate to form today’s extremely complex global supply chains. Effective digital infrastructure is necessary for every firm to coordinate and oversee supply chain activities like:
- Goods tracking.
- Supplier invoicing.
- Production updates.
- Supplier auditing.
5. Human resource management
Enterprise application software for human resource (HR) management is typically made up of tools to oversee and control HR functions like:
- Recruitment and training.
- Annual leave management.
- Payroll.
- Talent retention and engagement.
SOME USES OF ENTERPRISE SOFTWARE
1. Customer service
Enterprise software is used by businesses to increase client interaction and provide effective customer care. For instance, Intuit, a pioneer in financial software, combined several consumer communication channels, including chat, messaging, and the web, into an omnichannel cloud contact center by utilizing Amazon Connect. Thus, Intuit is able to provide prompt assistance to over 16.5 million consumers who reach out to them with financial inquiries each year. To ensure effective customer service, all agents see the same set of data.
2. Communication
Enterprise application software enhances communication between internal and external parties by automating processes, managing data, and making the best use of available network resources. For instance, the world’s largest streaming service Netflix replaced their internal email system with Amazon Simple Email Service (Amazon SES) in order to address issues with communication like:
- Optimizing email service for each Internet Service Provider
- Reducing the overhead of running dedicated email servers
- Scaling globally for wider customer reach
3. Sales and marketing
Enterprise level software can reduce silos between sales and marketing, so companies respond faster to the first contact new customers make. For example, technology services provider World Wide Technologies achieves sales efficiency by responding to initial customer requests with a quote management application.
4. Operation support
Enterprise software can save businesses thousands of dollars by reducing operational inefficiencies. For instance, Domino’s is enhancing service delivery by utilizing AWS corporate software solutions. Domino’s used Amazon SageMaker to create machine learning (ML) models that could precisely anticipate which pizza a consumer would order next, as online orders account for more than 70% of the company’s sales. The strategy improved customer satisfaction ratings while cutting down on pickup and delivery times.
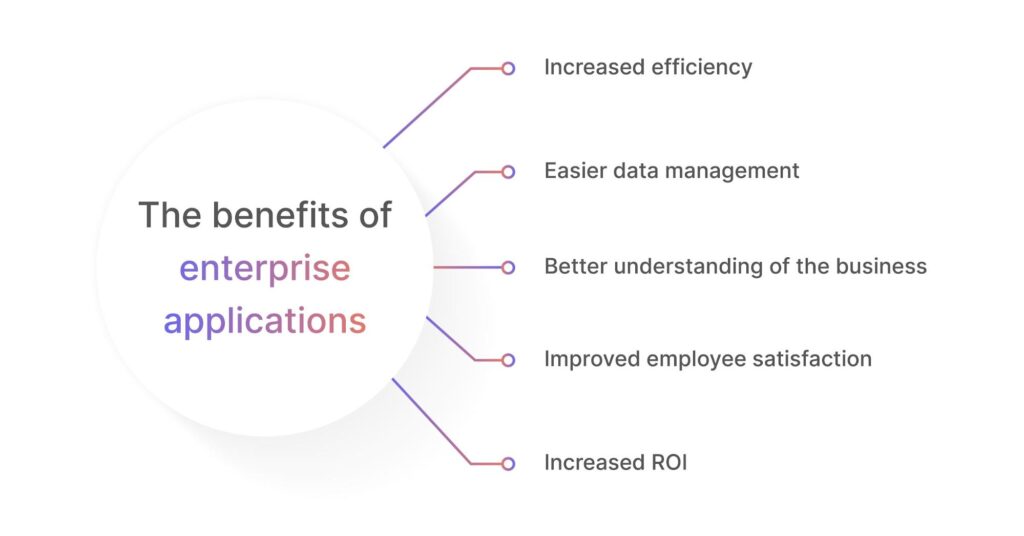
CONCLUSION
Enhanced communication, simpler procedures, better data management, increased operational efficiency, and improved decision-making abilities are a few of these. Enterprise software offers real-time insights into business processes, integrates disparate systems and departments, and automates repetitive work.
